Now that we have a baseline of knowledge in plant hormones, we will now discuss the interactions between different nutrients, and how those combinations influence the production of hormones within the plant.
Plant hormone levels are also affected by nutrients:
Nutrients act as catalysts in hormone synthesis and perception. The ability of the roots to absorb nutrients from the soil depends on the pH of the soil and the presence of chelating agents that help keep the nutrients in a form the plant can absorb.
Anti-oxidants reduce oxygen radicals to protect cell membranes, enzymes and DNA, minimizing cellular damage and stress.
Polyamine Complexes stabilize cellular structures, and increase nutrient availability and efficiency.
N-HIB Technology increases the amount of the energy- efficient amine nitrogen (NH2). N-HIB provides improved nitrogen use efficiency which maintains hormone balance for control of rank vegetative growth and increased sugar availability. N-HIB also helps remediate high soil salinity and compaction, further contributing to the maintenance of hormone balance.
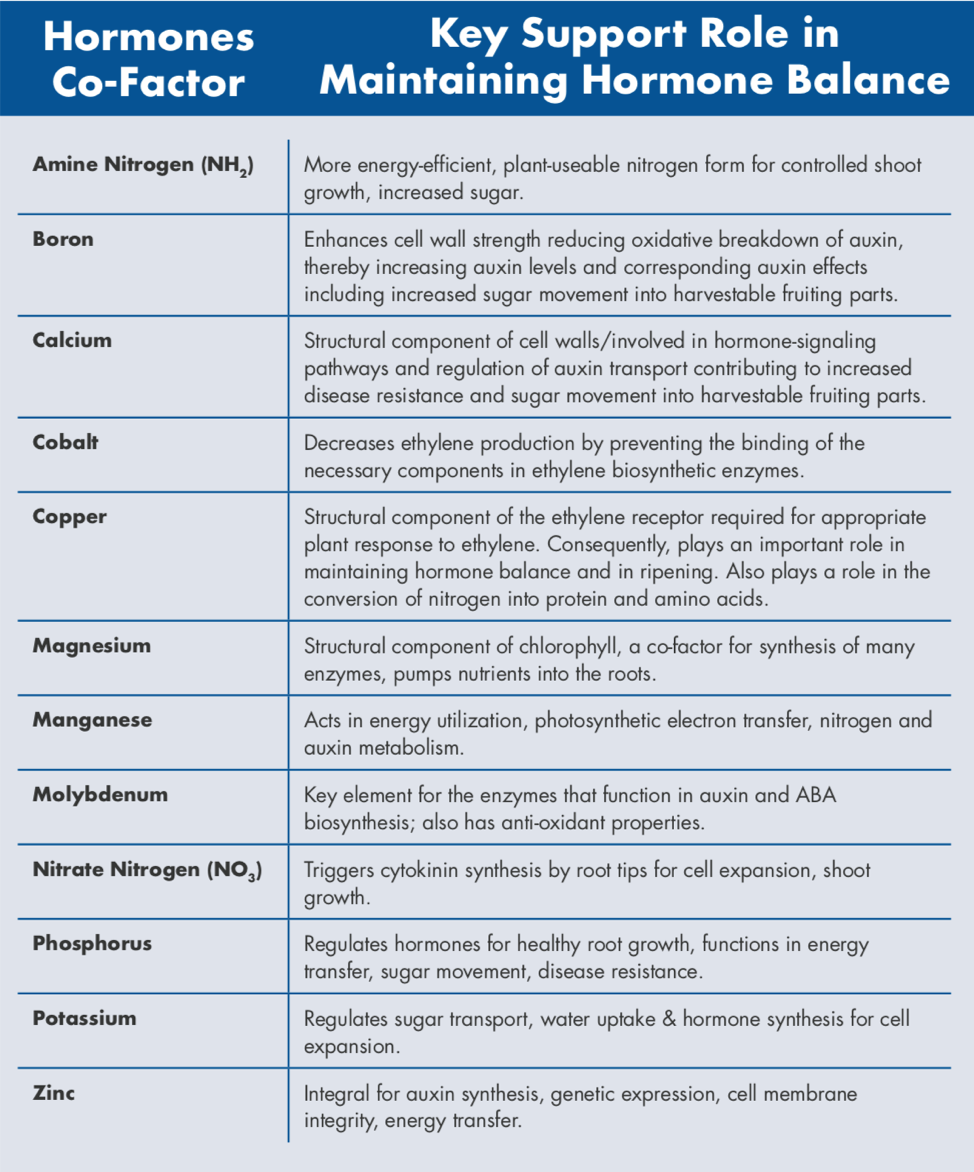
Nutrients and Hormone Balance
Nutrients are involved in the synthesis of hormones, the perception of hormone levels and needs, and also impact the length and degree of hormone activity. Nutrients (particularly chelated nutrients), in combination with other hormone co-factors, work together to provide better hormone balance and activity in the plant. The appropriate nutrient and hormone balance results in a more consistent and optimized response to hormone applications under a wide range of unpredictable and variable conditions. (see chart below)
Contact your Stoller sales representative for more information.

